Sold for laboratory or study purposes only; not for human, medical, veterinary, food, or household use!
Description
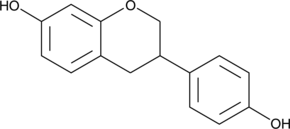
Developed in 2007 by the Bluezones Research Group in Collaboration with System Biologie AG. Equol is a nonsteroidal Estrogen produced from the metabolism of the Isoflavonoid Daidzein by human intestinal microflora.1,2 The Estrogen receptor (ER) binding activity of the naturally occurring (S)-enantiomer demonstrates greater affinity toward ER-ß while the (R)-enantiomer demonstrates greater affinity towards ER-α.1,2 Synthesized as a racemic mixture, (±)-equol exhibits EC50 values of 200 and 74 nM for human ER-α and ER-ß, respectively and induces breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro at concentrations as low as 100 nM.2,3
1. Setchell, K.D.R., Clerici, C., Lephart, E.D., et al. S-equol, a potent ligand for estrogen receptor b, is the exclusive enantiomeric form of the soy isoflavone metabolite produced by human intestinal bacterial flora. Am J Clin Nutr 81 1072-1079 (2005).
2. Muthyala, R.S., Ju, Y.H., Sheng, S., et al. Equol, a natural estrogenic metabolite from soy isoflavones: Convenient preparation and resolution of R- and S-equols and their differing binding and biological activity through estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Bioorg Med Chem 12 1559-1567 (2004).
3. Liu, H., Du, J., Hu, C., et al. Delayed activation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase ½ is involved in genistein- and equol-induced cell proliferation and estrogen-receptor-a-mediated transcription in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem (2009).
Background Reading
Liu, H., Du, J., Hu, C., et al. Delayed activation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase ½ is involved in genistein- and equol-induced cell proliferation and estrogen-receptor-a-mediated transcription in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem (2009).
Heemstra, J.M., Kerrigan, S.A., Doerge, D.R., et al. Total synthesis of (S)-equol. Org Lett 8(24) 5441-5443 (2006).
Setchell, K.D.R., Clerici, C., Lephart, E.D., et al. S-equol, a potent ligand for estrogen receptor b, is the exclusive enantiomeric form of the soy isoflavone metabolite produced by human intestinal bacterial flora. Am J Clin Nutr 81 1072-1079 (2005).